Detailed Description
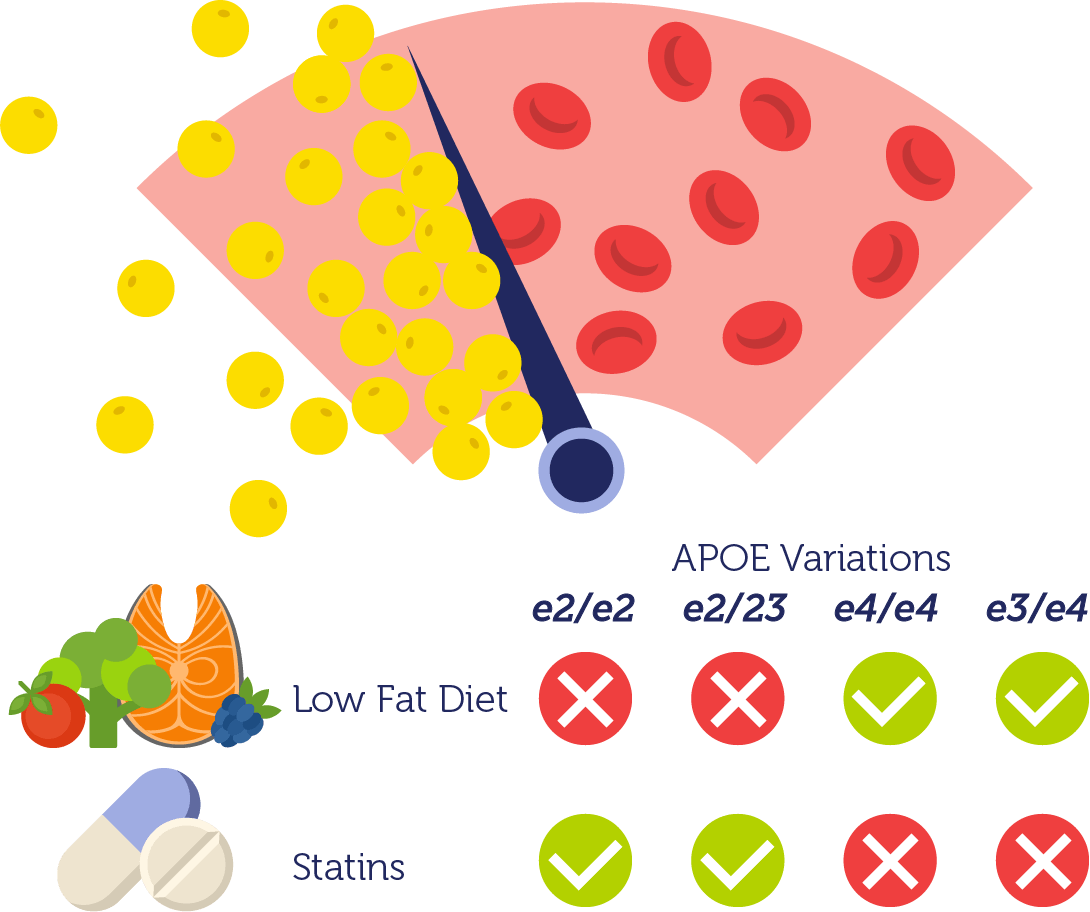
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) include heart attack and stroke. Maintaining normal cholesterol levels is essential for the prevention of CVD.
LDL-cholesterol is often referred to as the “bad” cholesterol. It collects in the walls of your blood vessels, where it can cause blockages and scarring known as atherosclerosis. Increased LDL-cholesterol levels put you at greater risk for CVD.
Other contributing factors to CVD include elevated triglycerides (the main form of storage fat in our body) and high levels of other low-density lipoproteins (e.g. beta-very low-density lipoproteins).
Hyperlipoproteinemia type III is one disease characterized by elevated triglycerides and beta-very low-density lipoproteins. It is associated with an early onset of peripheral vascular disease and CVD.