Detailed Description
The “promiscuity” gene is a genetic variant of the DRD4 gene, associated with an increased likelihood of sexual promiscuity.
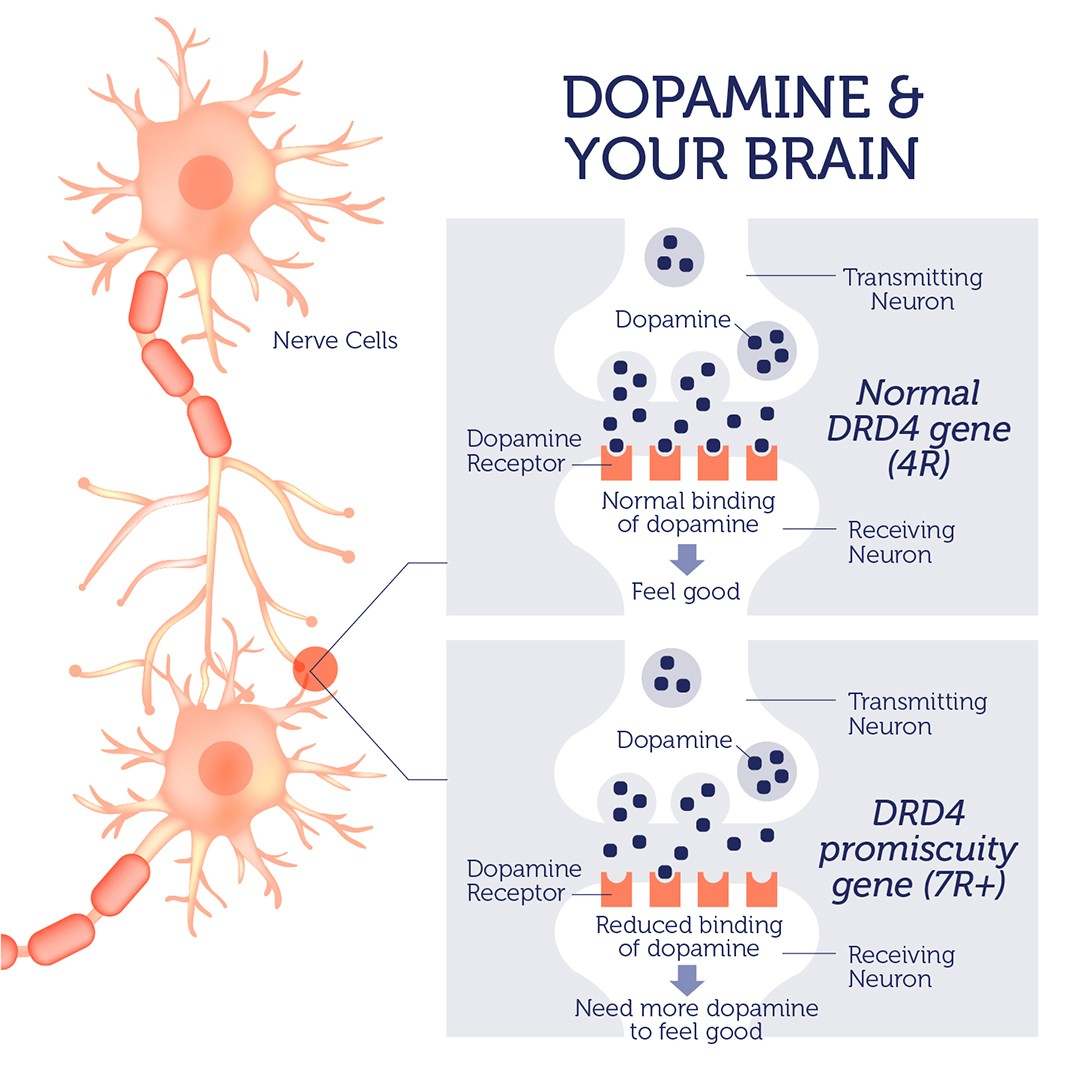
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter or a chemical made in the brain that gives us feelings of reward and pleasure. The dopamine receptor D4, encoded by the DRD4 gene, binds dopamine and transmits the signal into the cells.
The “promiscuity” gene is also known as the 7R+ version of the dopamine receptor. Altered receptors encoded by these variants bind dopamine less efficiently, compared to the common 4R version. As a result, reduced levels of the dopamine “feel good” signal is transmitted in the brain.
People with the 7R+ variants require higher levels of dopamine to achieve the same “good feeling” affects, and intriguingly sexual activity is a proven way to increase dopamine levels.